
DRONE INSPECTION
Inspecting structures and facilities is critical to ensuring the safety, efficiency and longevity of buildings and equipment of all types. However, traditional methods are often expensive, time-consuming and risky.
Drone technology is an innovative solution that transforms this reality by providing faster, safer and more detailed inspections.
Find out how drone inspection is revolutionising structural analysis and maintenance, and discover its main applications.
Drones, equipped with high-resolution cameras and advanced sensors, offer several advantages over conventional inspection methods:
-
Safety: Inspecting tall structures, such as telecommunications towers or chimneys, poses significant risks to workers. Drones eliminate the need to climb to dangerous heights, drastically reducing the risk of accidents.
-
Time and Cost Savings: Drone inspections are significantly faster, reducing downtime for the structures under review. Furthermore, operating costs are lower, as there is no need for scaffolding, cranes, or heavy equipment.
-
Access Hard-to-Reach Areas: Drones can access areas that are inaccessible or dangerous to humans, such as confined spaces, sloping roofs, or collapsed areas.
-
Accurate and Detailed Data: Equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors, drones capture detailed data that allows for thorough analysis. This data can be used to create 3D models, heat maps, and accurate reports.
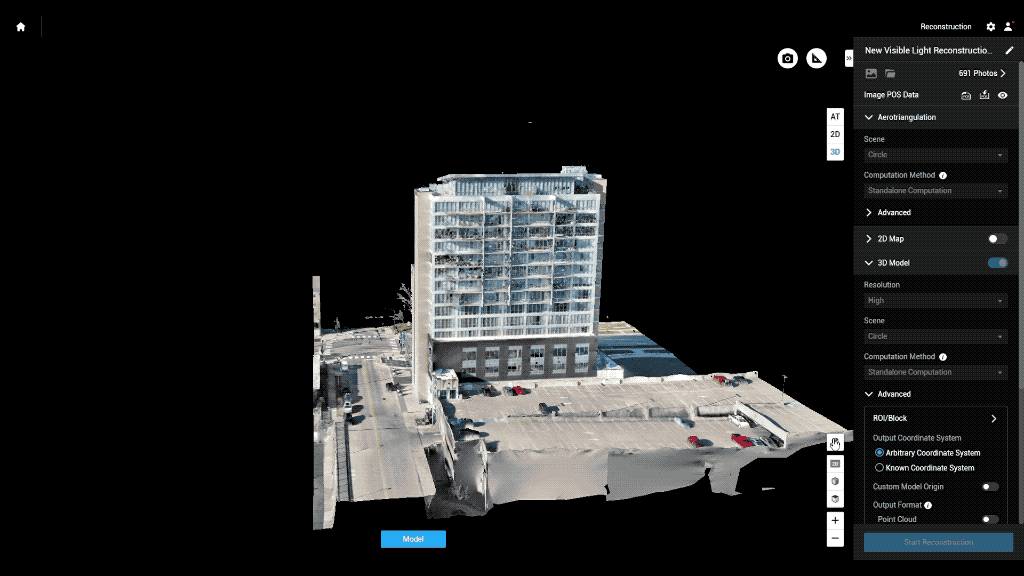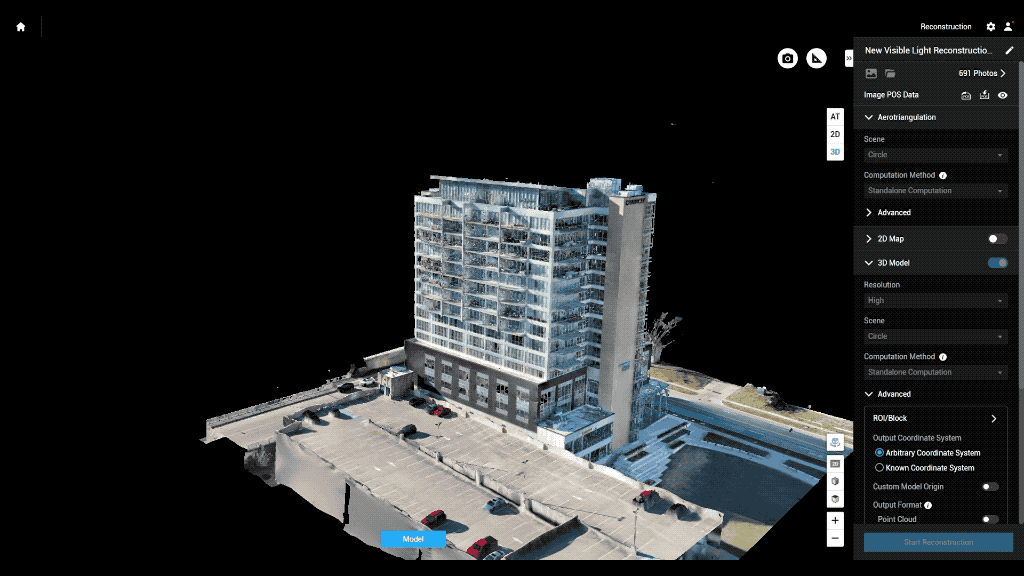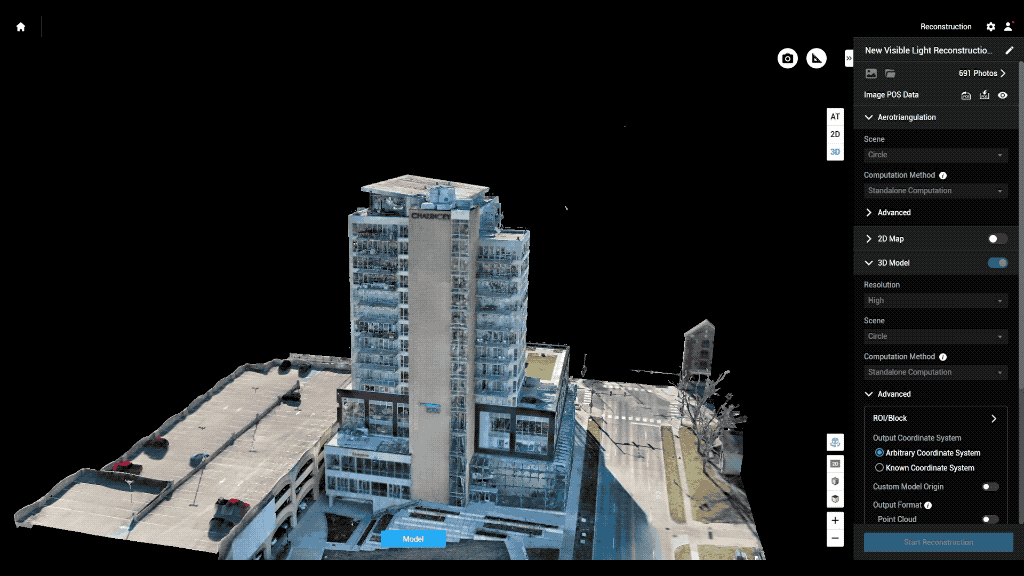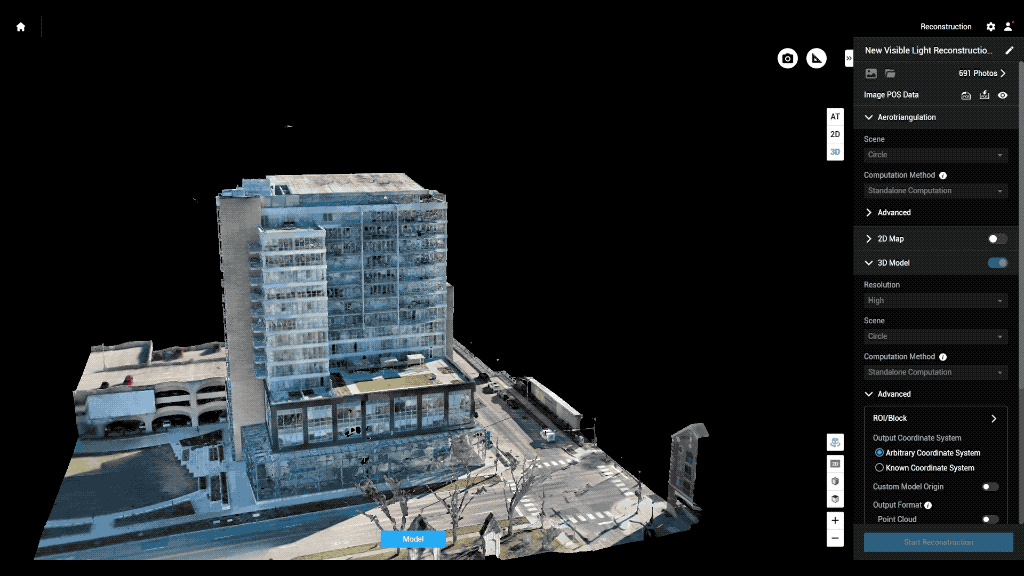
Main drone inspection applications:
Roofs, Slabs, and Coverings:
Damage and wear detection: Drones can identify roof damage, such as broken tiles, leaks and worn areas, eliminating the need for physical inspection and saving time and money.
Thermal analysis: Thermal sensors can detect hot spots that indicate leaks or inadequate insulation.
Facades:
Structural assessment: Drones can be used to inspect the exterior of tall buildings, identifying cracks, corrosion and other structural issues.
Preventive maintenance: Regular drone-based inspections help to identify problems before they become serious, facilitating preventive maintenance.
Construction and Building Works:
Progress monitoring: Using drones to track construction progress enables project managers to verify schedule compliance and identify issues with execution.
Comparing with BIM projects: Integrating drone data with BIM (Building Information Modelling) models ensures construction aligns with the original design.
Solar Panel:
Defect detection: Identifies defective or dirty cells in solar panels to optimise system efficiency.
Maintenance and cleaning: Accurate data helps to schedule maintenance and cleaning more efficiently.
Electricity and Telecommunications Towers:
Component inspection: Drones can be used to inspect cables, insulators and other components of electrical and telecommunications towers, identifying any wear or damage.
Access to Remote Areas: They can inspect towers in hard-to-reach areas, ensuring that all infrastructure is regularly assessed.
Chimneys, Silos, and Ducts:
Internal and external inspection: Drones can be used to inspect the interior and exterior of chimneys, silos and ducts, identifying corrosion, blockages and other issues.
Safety and compliance: They ensure that these structures comply with safety and operating standards.
Inspection of Treatment Plants:
Structure monitoring: Drones can be used to inspect tanks, basins and other structures at water and wastewater treatment plants.
Leak and wear detection: Problems can be detected before they cause service interruptions or environmental damage.
Critical Infrastructure Inspection:
Bridges and viaducts: Regular inspections ensure that they are in good condition, preventing accidents and collapse.
Historic buildings: Drones can be used to inspect hard-to-reach areas of historic buildings and detect structural damage.






